Critical thinking is a vital skill that helps us analyse information, make informed decisions, and solve problems effectively. It involves evaluating evidence and questioning our assumptions to reach sound conclusions. This ability is essential not only in academic settings but also in our everyday lives, as we navigate a world filled with complex information and diverse perspectives.

By embracing critical thinking, we empower ourselves to interpret data accurately and recognise biases that may influence our thinking. It also enables us to articulate our thoughts clearly and engage in meaningful discussions. As we learn to apply these skills, we enhance our problem-solving capabilities and decision-making processes in various domains.
As we explore the essence of critical thinking, we will uncover the skills necessary for effective analysis and apply the RED Model. This journey will help us appreciate the importance of being critical thinkers in our society, especially in an age where media and advertising shape our perceptions daily.
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking enhances our ability to make sound decisions.
- Understanding cognitive processes helps improve our thinking skills.
- Applying critical thinking is crucial in various areas of our lives.
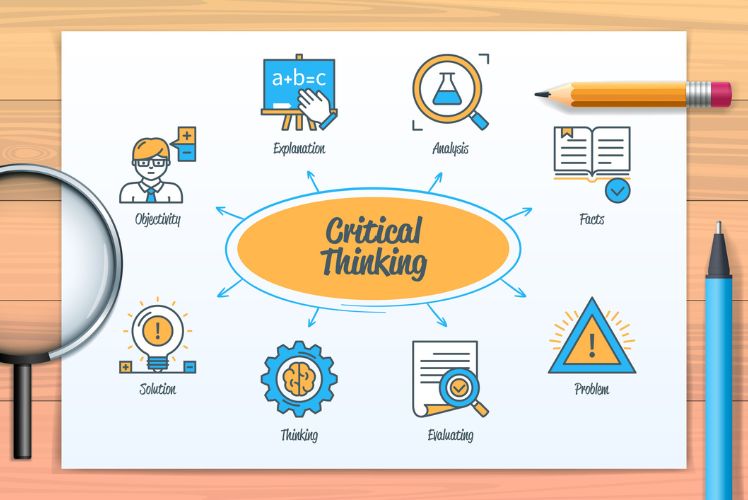
The Essence of Critical Thinking

Critical thinking involves applying reasoning skills to analyse information objectively. This practice has roots in ancient philosophy, marked by the ideas of influential thinkers like Socrates and Plato. Understanding its essence is pivotal to developing our own critical abilities.
Defining Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally. It involves analysing facts, questioning assumptions, and evaluating evidence. We engage in this process to reach sound conclusions and make informed decisions.
Key skills of critical thinking include:
- Analysis: Breaking down complex information.
- Evaluation: Assessing the credibility of sources.
- Inference: Drawing logical conclusions from available data.
By honing these skills, we can approach problems more effectively and offer solutions that are well-reasoned and justified.
Notable Historical Perspectives
The foundations of critical thinking trace back to ancient philosophers like Socrates and Plato. Socrates is known for his Socratic method, which encouraged asking probing questions to stimulate critical thinking and illuminate ideas. This dialogue style fosters deeper understanding.
Plato, a student of Socrates, expanded on these ideas. He believed that through reasoned debate and dialogue, individuals could discover truths and develop their understanding. Their contributions set the stage for modern critical thinking, emphasising the importance of questioning and logical reasoning in our pursuit of knowledge.
Essential Skills for Effective Critical Thinking

To develop our critical thinking abilities, we focus on several essential skills. These skills help us analyse information, evaluate arguments, and regulate our own thought processes. By honing these skills, we can better understand complex issues and make informed decisions.
Identification and Analysis
We start by identifying the main arguments and evidence presented in any situation. This involves careful reading and listening. We look for key points that support or oppose a claim. Next, we analyse this information by breaking it down into smaller parts.
This analysis helps us to see connections between ideas. We ask questions like: What is the author's purpose? Are there any biases present? Can we trust the sources of information? By considering these aspects, we sharpen our ability to assess the reliability of the evidence.
Evaluation and Inference
After identifying and analysing arguments, we move on to evaluation. This process involves making judgments about the quality and relevance of the information. We weigh the strengths and weaknesses of different perspectives.
In this stage, we also draw inferences—conclusions based on the evidence available. We ask ourselves: What can we reasonably conclude from the facts? Are there any logical fallacies in the arguments? This careful reasoning helps us form sound opinions based on evidence rather than assumptions.
Explanation and Self-Regulation
Finally, we focus on explanation and self-regulation. Explaining our thought process clearly to others is vital. We must articulate our reasoning and the evidence supporting our conclusions. This clarity can improve discussions and help others understand our viewpoint.
Self-regulation is about monitoring our own thinking. We reflect on our biases and assumptions. By being aware of them, we can adjust our reasoning. This skill is essential for ensuring that our thoughts remain fair and objective. Critical thinking is not just about what we think, but how we think.
The RED Model of Critical Thinking

The RED Model is a vital framework that enhances our critical thinking skills. By focusing on recognising assumptions, evaluating arguments, and drawing conclusions, we can improve our decision-making processes and minimise unconscious bias that may affect our judgement.
Recognise Assumptions
The first step in the RED Model is to recognise assumptions. Assumptions are beliefs we hold without questioning. They can be conscious or unconscious. By identifying these assumptions, we can better understand our viewpoint and avoid biases.
To do this, we can ask ourselves questions such as:
- What am I assuming here?
- Why do I believe this to be true?
This process helps us to uncover potential biases influencing our thoughts. Recognising assumptions creates a foundation for a more objective perspective, leading to clearer reasoning.
Evaluate Arguments
Next, we need to evaluate arguments. This involves examining the evidence behind a claim. We should consider the quality and relevance of the information presented. Are the sources credible? Do the arguments logically connect?
We can use a few strategies here:
- Check for logical fallacies.
- Assess the validity of the evidence.
Effective evaluation helps us separate strong arguments from weak ones. By doing so, we can recognise when our own biases might cloud our judgement. This critical evaluation process is essential for making informed decisions.
Draw Conclusions
The final step in the RED Model is to draw conclusions. After recognising assumptions and evaluating arguments, we synthesise our findings. Here, we decide what we believe to be true based on the evidence.
To draw well-founded conclusions, we should:
- Reflect on the information gathered.
- Consider alternative viewpoints.
- Acknowledge any biases we may still hold.
This step is crucial for ensuring our conclusions are reasonable and sound. By drawing conclusions thoughtfully, we can enhance our critical thinking skills and improve our overall reasoning abilities.
Cognitive Processes and Developing Critical Thinking

Understanding cognitive processes is key to improving our critical thinking skills. We can actively engage in methods that promote better decision-making and problem-solving abilities. By focusing on development and practical exercises, we enhance our thinking capabilities.
Critical Thinking Development
Developing critical thinking involves several cognitive processes. We need to analyse information, evaluate arguments, and consider various viewpoints. This requires us to be aware of our thought patterns and biases.
Metacognition plays a vital role here. It helps us monitor and control our thinking. Being conscious of our reasoning allows us to adjust our approaches for better outcomes.
Incorporating structured thinking techniques also fosters development. For example, using the Socratic method promotes dialogue and questioning. This approach stimulates deeper analysis of issues. We can practice by discussing real-life scenarios, allowing us to refine our thought processes.
Exercises and Best Practices
Engaging in specific exercises can strengthen our critical thinking. Simple activities can include debating different sides of an argument or analysing news articles for bias.
Additionally, we can use mind mapping to organise ideas visually. This helps us break down complex concepts into manageable parts.
Another effective practice is reflective journaling. Writing about our thoughts and decisions encourages us to question our reasoning and learn from our experiences.
Group discussions are beneficial as well. They promote diverse perspectives and help us articulate our ideas clearly. Through these practices, we can systematically develop our critical thinking skills.
Critical Thinking in Different Domains
Critical thinking plays a vital role across various fields, allowing us to make reasoned decisions and solve problems effectively. Understanding how critical thinking is applied in different domains can enhance our approach to challenges in business, education, health, and science.
Business and Entrepreneurship
In business, critical thinking enables us to evaluate information and make strategic decisions. We analyse market trends, assess risks, and identify opportunities based on factual data and conceptual understanding.
Key skills include:
- Problem-solving: We identify issues and consider multiple solutions.
- Decision-making: We weigh pros and cons to make informed choices.
- Innovation: We use creative thinking to develop new products or services.
Taking time to question assumptions and analyse competitors helps us maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace. Critical thinking is indeed essential for entrepreneurs aiming to navigate uncertainties and build successful ventures.
Education Systems
In education, critical thinking is fundamental for developing analytical skills in students. We foster an environment where students learn to question information, evaluate various viewpoints, and articulate their thoughts clearly.
Effective strategies involve:
- Encouraging debate: Students engage in discussions, presenting arguments for and against different ideas.
- Promoting project-based learning: This method allows learners to apply critical thinking skills to real-world problems.
- Assessing understanding: We regularly evaluate students’ grasp of concepts through critical reflection.
By integrating critical thinking into curricula, we prepare students for challenges beyond the classroom, building lifelong learners capable of adapting to an ever-changing world.
Scientific Research
In scientific research, critical thinking is crucial for formulating hypotheses, designing experiments, and interpreting data. We must remain sceptical and question our findings to ensure reliability and validity.
Important aspects include:
- Analysis of data: We use statistical tools to interpret results accurately.
- Peer review: Collaborating with peers helps identify flaws in our methods and conclusions.
- Ethical considerations: Assessing the implications of our research is vital to maintain integrity.
Through critical thinking, we ensure that scientific discoveries are based on sound reasoning, fostering innovation in various scientific disciplines.
Health and Medicine
In health and medicine, critical thinking is essential for diagnosing conditions and planning treatment. We evaluate symptoms, medical histories, and research to make informed decisions about patient care.
Key components consist of:
- Clinical reasoning: We assess the reliability of sources and evidence-based guidelines.
- Patient-centred care: Listening to patients helps us understand their needs and concerns.
- Continuous learning: We remain open to new information and evolving best practices.
By employing critical thinking, healthcare professionals enhance patient outcomes and contribute to more efficient healthcare systems. This approach ensures that we provide the best possible care while adapting to advancements in medical science.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Effective decision-making and problem-solving are key skills that can enhance our critical thinking ability. These skills help us evaluate situations, consider alternatives, and choose the best path forward. In this section, we will explore rational decision-making and strategic problem-solving approaches that can aid us in these processes.
Rational Decision-Making
Rational decision-making is a systematic process that involves several steps. First, we identify the problem clearly. Next, we gather relevant information and assess our options.
After evaluating the alternatives, we weigh their pros and cons. This helps us understand the consequences of each choice. Finally, we make a decision and implement it, followed by evaluation to see if it meets our expectations.
This method allows us to make choices based on logic rather than emotions, ensuring more consistent outcomes. By practising rational decision-making, we strengthen our critical thinking ability, which is crucial in both personal and professional settings.
Strategic Problem-Solving Approaches
In problem-solving, we often face challenges requiring careful thought and strategy. One effective approach is to use the “define, explore, develop” method.
- Define the problem: Clearly state what the issue is.
- Explore options: Brainstorm possible solutions without judgement.
- Develop a plan: Choose the best solution and create a step-by-step plan to implement it.
We can also use tools like decision matrices to compare options visually. This helps clarify our choices and ensures we consider all factors.
Utilising these strategic approaches can lead to better solutions and enhance our ability to respond to problems effectively. This not only improves our decision-making but also equips us to tackle unexpected challenges.
Influence of Media and Advertising on Critical Thinking
Media and advertising play a significant role in shaping our thoughts and decisions. By understanding how these elements influence critical thinking, we can better navigate the complex information we encounter daily.
Navigating Media Information
In today's digital world, we are constantly bombarded with information from various media sources. It's crucial for us to develop skills to navigate this landscape effectively.
We need to assess the credibility of the sources we encounter. This involves asking questions like:
- Who created the content?
- What are their motives?
- Are they presenting evidence to back up their claims?
By being aware of these considerations, we can enhance our media literacy. This helps us discern fact from opinion, allowing for better critical thinking.
Studies suggest that short interventions can improve our ability to analyse media. For instance, workshops can raise awareness about misleading information and encourage us to think critically about the media we consume.
Analysing Advertising Content
Advertising is designed to persuade us, often using emotional tactics and appealing visuals. Understanding these techniques is essential for developing our critical thinking skills.
When we analyse advertisements, we should consider the following elements:
- Target Audience: Who is the ad aimed at?
- Message: What is the ad trying to communicate?
- Evidence: Does the ad provide solid proof of its claims?
For example, a recent study found that young people’s critical reasoning skills are still developing, making them more susceptible to persuasive advertising. By recognising these factors, we can make informed choices about the products and services we engage with.
This process of critical analysis fosters a more thoughtful approach to media consumption and advertising, allowing us to make smarter decisions.
Critical Thinkers in Society
Critical thinkers play an important role in shaping our society by analysing information, evaluating arguments, and making informed decisions. Their contributions affect various fields, including education, industry, and governance.
Roles and Responsibilities
In education, critical thinkers guide students towards deeper understanding. They encourage questioning and exploration, vital for developing reasoning skills. By promoting a classroom environment of inquiry, we foster future thinkers who can tackle complex problems.
In the workplace, critical thinkers evaluate strategies and improve decision-making. They analyse data and provide insights, helping teams innovate and adapt. Their ability to assess information leads to effective solutions, enhancing productivity.
In governance, critical thinkers hold leaders accountable. They scrutinise policies and advocate for transparency. By questioning assumptions and seeking evidence, they contribute to a more informed citizenry, promoting democracy and civic engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address common inquiries regarding critical thinking. This includes its core skills, importance in education, methods for development and assessment, and its role in decision-making and workplace productivity.
What are the core skills associated with critical thinking?
The core skills of critical thinking include analysis, evaluation, and inference. We need to be able to identify arguments, assess their validity, and draw reasoned conclusions based on evidence. These skills help us to think logically and approach problems methodically.
Why is critical thinking essential in educational settings?
Critical thinking is vital in educational settings because it fosters independent thinking and creative problem-solving. By encouraging students to evaluate information critically, we help them become more informed and engaged learners. This prepares them not just for exams, but for real-world challenges.
How can critical thinking be effectively developed and assessed?
To develop critical thinking, we can utilise various teaching methods such as Socratic questioning and problem-based learning. Assessment can be done through essays, presentations, and peer reviews that focus on reasoning and argumentation. These methods allow us to gauge how well students can apply their critical thinking skills.
What is the role of critical thinking in decision-making processes?
Critical thinking plays a significant role in decision-making processes by enabling us to weigh options and consider long-term outcomes. It helps us evaluate information critically, which leads to more informed choices. This is essential in both personal and professional contexts.
How do critical thinking abilities evolve with different levels of education?
As we progress through different levels of education, our critical thinking abilities typically become more advanced. Early education may focus on basic reasoning skills, while higher education encourages more complex analysis and synthesis of information. This evolution prepares us for increasingly challenging tasks.
In what ways does critical thinking influence workplace productivity and problem-solving?
In the workplace, critical thinking enhances productivity by promoting clarity and focus. It enables teams to identify issues quickly and develop effective solutions. By fostering a culture of critical thinking, organisations can improve collaboration and drive innovation.